

Most ebook files are in PDF format, so you can easily read them using various software such as Foxit Reader or directly on the Google Chrome browser.
Some ebook files are released by publishers in other formats such as .awz, .mobi, .epub, .fb2, etc. You may need to install specific software to read these formats on mobile/PC, such as Calibre.
Please read the tutorial at this link. https://ebooknice.com/page/post?id=faq
We offer FREE conversion to the popular formats you request; however, this may take some time. Therefore, right after payment, please email us, and we will try to provide the service as quickly as possible.
For some exceptional file formats or broken links (if any), please refrain from opening any disputes. Instead, email us first, and we will try to assist within a maximum of 6 hours.
EbookNice Team
Status:
Available4.6
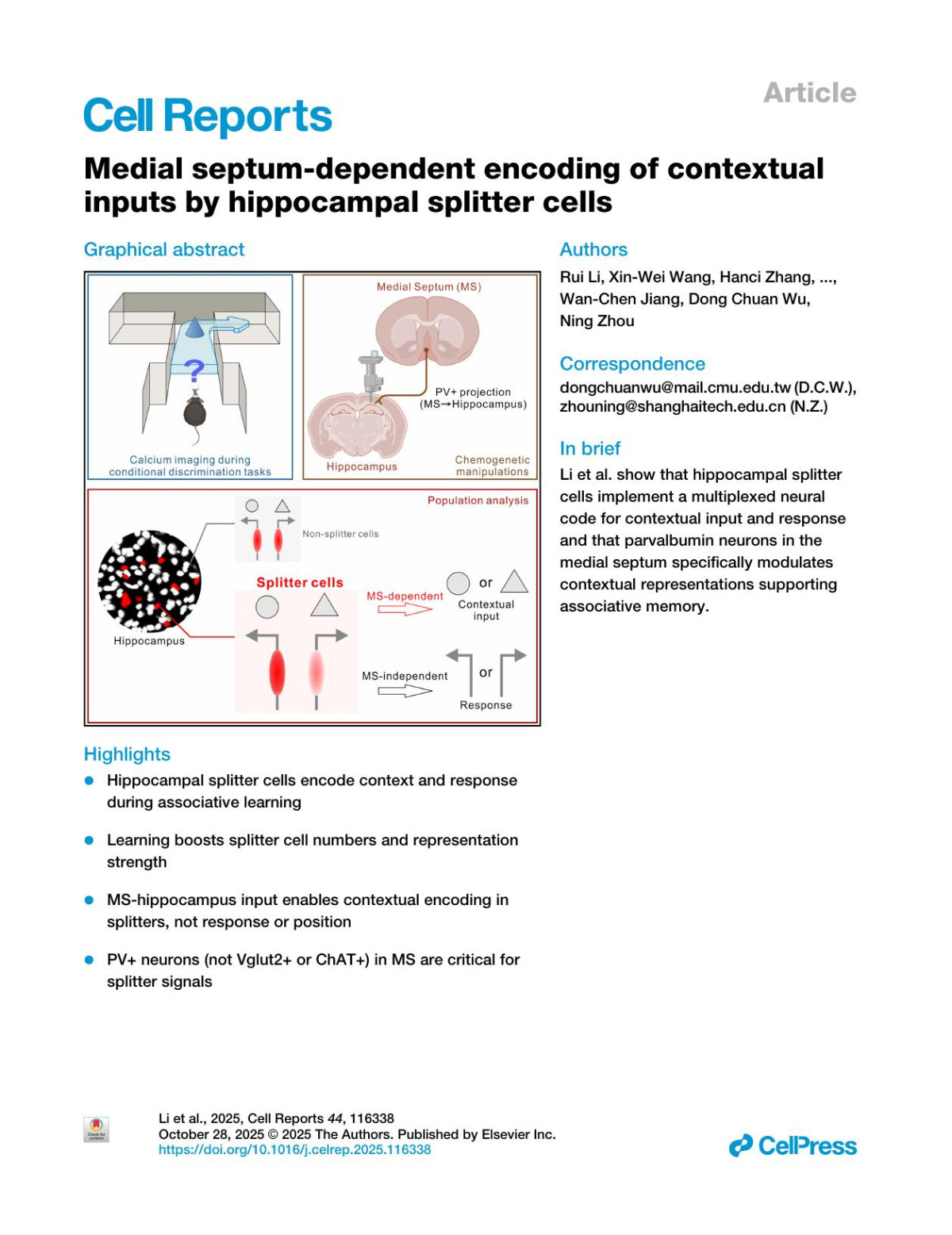
12 reviewsSUMMARY The brain’s ability to adapt to changing environments relies on encoding associations between stimuli and response strategies. Hippocampal splitter cells, which exhibit context-dependent firing patterns, are thought to contribute to this process, but whether they encode non-spatial contextual information and the neural circuits supporting such representations remains unclear. Using in vivo calcium imaging, we record dorsal hippocampal activity in mice performing a conditional discrimination task. Splitter cells encode both contextual input and response information in a dissociable manner, with their numbers and task-specific representations increasing during learning. Selective inhibition of the medial septum (MS) pathway or parvalbumin expressing neurons in the MS reduces behavioral accuracy and decreases splitter cell numbers. MS inactivation specifically disrupts contextual representation without affecting response-related encoding. These findings demonstrate that splitter cells rely on distinct circuits to encode different components of the associative structure, with the MS critically supporting contextual inputs required for flexible behavior.